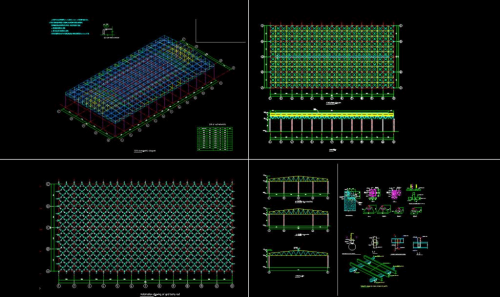
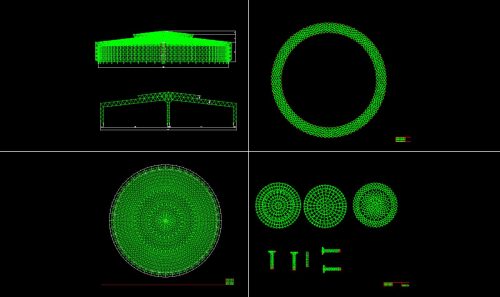
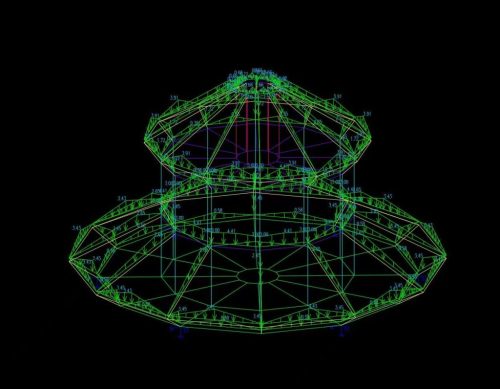
Space frame lattice fabrication primarily involves the factory-based production of nodes (bolted or welded) and rods. This is a refined and standardized process.
I. Core Component Processing
- Bolted-Ball Node Processing
This is currently the most widely used node type, requiring extremely high machining precision.
Process Flow:
Raw Material Preparation: Use high-quality round steel (usually 45-gauge steel) with certified material quality.
Cutting: Saw the round steel into billets slightly larger than the diameter of the ball blank.
Forging the Blank: After heating, the billet is forged into a spherical blank on a forging press. This step eliminates internal defects and refines the grain size.
Normalizing: Normalizing the forged ball blank to eliminate forging stresses and uneven microstructure, improving cutting performance.
Machining the Reference Hole: Machine the reference threaded hole (usually a horizontal hole) on a CNC drill.
CNC Machining Each Screw Hole:
This is the most critical step. The ball blank is secured to a dedicated indexing head. According to the design drawings, the CNC system controls the indexing head's rotation angle (accurate to the second) to determine the orientation of each hole.
Drilling and tapping (internal threading) are then performed to create high-strength bolt holes.
The thread accuracy, perpendicularity, and hole depth of each hole are rigorously inspected.
Numbering: Each processed bolt ball is uniquely numbered to facilitate assembly with the corresponding rod.
Anti-corrosion treatment: Hot-dip galvanizing or spray-coating with anti-rust paint is typically used. Acid cleaning and rust removal are required before galvanizing, and the zinc coating thickness must meet the required requirements after galvanizing.
Key Quality Control Points:
Diameter deviation (±0.2mm)
Thread accuracy (must be checked with a go/no-go gauge)
Angle deviation between adjacent screw holes (±30°)
Dimensional deviation between the screw hole end face and the ball center
Zinc coating thickness and uniformity
- Processing of Welded Hollow Sphere Nodes
This is suitable for nodes subject to high loads or with a large number of rods.
Process Flow:
Cutting: The steel plate is cut into round billets. Heating and Pressing: The round blank is heated to a plastic state and pressed into a hemispherical shape in a mold.
Trimming and Beveling: The edges of the pressed hemisphere are cut and the welding groove is machined.
Assembly and Welding: The two hemispheres are assembled and butt-welded along the groove. Welding is typically performed using CO₂ gas shielded welding or submerged arc welding, requiring full penetration.
Nondestructive Testing (NDT): 100% ultrasonic testing (UT) is performed on the weld seam to ensure that there are no internal defects such as cracks and lack of fusion. This is critical to ensuring safety.
Numbering and Corrosion Protection: Same as above.
- Rod Fabrication
Rods are typically round steel tubes, welded to end caps or tapers at both ends.
Process Flow:
Cutting: The steel tube is cut to the designed length using a band saw or intersecting wire cutting machine. Length tolerances are very tight (typically ±1.0mm).
End Fabrication: End caps or tapers are welded to both ends of the rod. The cone head is used to connect to the bolt ball, and its end needs to be milled flat to ensure a smooth contact surface with the bolt ball.
Welding: Weld the cover plate/cone head to the steel pipe. This weld is a critical load-bearing weld and must be full and meet the design weld grade.
Trial Assembly (Pre-Assembly):
This is an extremely important step! Bolt balls and members from the same unit (e.g., a cone) are randomly selected and trial-assembled in the factory using a wrench.
This is to verify that the screw holes are aligned, the bolts can be inserted smoothly, the member length is accurate, and the overall unit dimensions are within tolerance.
This effectively avoids the serious problem of "unable to assemble" on site.
Numbering: Each member is labeled or written with a number at both ends to indicate its location (e.g., "A1-B2" indicates the web member from the upper chord node A1 to the lower chord node B2).
Anti-Corrosion Treatment: Hot-dip galvanizing or painting is performed simultaneously with the nodes. Take care to protect the threads of high-strength bolt holes (on the cover plate or tapped head) to prevent galvanizing from clogging the threads (a tap back-tap is often used to clean this).
II. Overall Process and Management of Space Frame Grid Fabrication
Drawing Detailing and Review: After receiving the design drawings, the fabrication shop will refine them, generating detailed fabrication drawings and material lists, which will be confirmed by the original design company.
Raw Material Procurement and Inspection: Steel pipes, steel plates, round steel, high-strength bolts, etc. that meet the design requirements are purchased. All incoming materials must be accompanied by a quality assurance certificate and undergo sampling and re-inspection as required (such as mechanical property testing).
Production Planning and Process Briefing: A production plan is developed, and technical briefings are provided to workers at each process, clarifying process requirements and quality standards.
Workshop Processing: All components are produced according to the above process.
In-Process Inspection and Final Inspection:
IPQC (In-Process Quality Control): Quality inspectors conduct inspections after each process (such as thread inspection, weld visual inspection, and rod length inspection). FQC (Final Quality Control): After all parts are processed, they undergo a comprehensive dimensional, visual, and corrosion resistant coating inspection.
Marking, Packaging, and Shipping:
All components are divided, categorized, labeled, and packaged according to the order of installation.
Small parts such as bolts and screws are packed in iron boxes to prevent loss.
Rods and ball joints are typically bundled for shipment, and measures must be taken during the shipment process to prevent deformation and coating wear.
III. Core of Quality Control (Summary)
Precision: The accuracy of rod length and screw hole angles is a prerequisite for smooth on-site installation.
Weld Quality: Welds on ball joints and rod ends directly impact structural safety and must undergo non-destructive testing.
Material Quality: The mechanical properties of raw materials and high-strength bolts must meet 100% quality standards.
Corrosion Protection Quality: The hot-dip galvanizing process and thickness determine the durability of the structure.
Traceability: A unique numbering system for each component ensures traceability from drawing to installation. Space frame fabrication is a typical industrialized process of "factory prefabrication, on-site installation," offering superior quality compared to on-site handcrafting. Choosing a fabricator with advanced CNC equipment, a strict quality management system, and extensive experience is fundamental to the success of a space frame project.